What is Bacitracin Susceptibility Test ?
- Bacillus licheniformis produces bacitracin, which prevents the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a significant component of the bacterial cell wall.
- When bacitracin is present, it prevents bactoprenol from transferring NAM and NAG sugars across the cell membrane, preventing peptidoglycan formation.
- The most common way to distinguish beta hemolytic Group A streptococci from beta hemolytic non-Group A streptococci is to test for bacitracin sensitivity.
- Due to the difficulties in doing sero-grouping and the expensive cost of antisera, many laboratories employ this test as the sole test for diagnosing GAS infections.
- Antimicrobial susceptibility tests are commonly used to distinguish between different species of the same genus.
- Antimicrobial discs are used to test bacteria’s susceptibility to specific antibiotics.
- Bacitracin is a bactericidal medication that is rarely administered for systemic usage and is used to treat superficial skin infections.
Objectives of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- To distinguish beta-hemolytic Streptococci belonging to Group A (mainly S. pyogenes) from other beta-hemolytic Streptococci.
- To investigate the pattern of antibiotic susceptibility of various bacteria to Bacitracin.
Principle of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- Bacitracin disc (0.04) inhibits the development of Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci on blood agar.
- All coagulase-negative staphylococci are resistant to 0.04 units disc, as are micrococci and streptococci.
- Filter paper discs impregnated with 0.04 units of Bacitracin are used to assess susceptibility to Bacitracin. The impregnated discs are then placed on agar, allowing the antibiotic to spread into the media and stop the organism from growing.
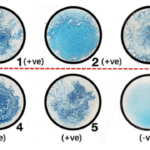
- The zone of inhibition detected around the discs is used to evaluate the test outcome after incubation.
- If the organism’s development reaches the disk’s edge, it is resistant, however the existence of a circular zone surrounding the disc indicates inhibition and susceptibility.
- When used as a screening test before serological grouping, bacitracin discs can save a lot of time, labour, and resources.
- Bacitracin sensitivity was shown to be higher in Group A Streptococci than in other beta-hemolytic strains.
- As a result, a Bacitracin susceptibility test using antimicrobial discs is recommended as a quick diagnostic tool for Group A Streptococci.
Microorganism tested
- Bacitracin susceptibility testing is used to distinguish Staphylococci from Micrococci in clusters of penicillin-susceptible or “sticky” Gram-positive cocci that are catalase-positive and coagulase-negative from invasive-site specimens.
- Lemon yellow colonies are not tested because Micrococcus is assumed to be present.
Media, Reagents, and Supplies Used in Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Media
- Blood agar or
- Mueller Hinton Agar
Supplies
- Bacitracin 0.04U disks
- Swabs
- Sterile forceps
- Broth for inoculation
Procedure of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
The Bacitracin Susceptibility Test can be performed in two ways, utilising two distinct nutritional medium. Pure cultures of an organism obtained via subculture or directly from clinical samples can be used for testing. The following are the procedures for two separate Bacitracin susceptibility tests:
Looking for Fully Funded PhD Positions: Click Here
Hebert’s method using Blood Agar plates
- The organism is prepared as a 0.1 McFarland suspension after an overnight culture.
- Lawn culture can be achieved by inoculating different portions of the blood agar plate. Each portion should be injected in one direction only, and the inoculation area should allow for a 10 mm spacing between each disc to be placed on the plate.
- The discs are placed on the agar with sterile forceps after drying for about 10 minutes. To guarantee adhesion, the discs are tapped with a sterile stick.
- The plates are then incubated for 24 hours at 35-37°C.
- The zone of inhibition is seen and measured after incubation. Serological tests can provide additional confirmation.
Mueller Hinton Agar method
- Mueller Hinton agar could also be used to test fast-growing organisms’ susceptibility.
- From the overnight culture of the organism, a 0.5 McFarland suspension is generated.
- The suspension is then injected into the MHA plates using sterile swabs to create bacterial lawns on the agar.
- The antibiotic discs are placed on the agar plates with sterile forceps after drying for about 10 minutes, allowing a gap of about 10 mm between the discs.
- To ensure that the discs adhere to the plates, they are tapped with a sterile stick.
- The inverted plates are then incubated at 35-37°C for 24 hours.
- The inhibitory zone is measured and observed. Serological tests can provide additional confirmation.
Result Interpretation of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Image Source: Bailey and Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology. Elsevier.
[ninja_tables id=”3902″]
Uses of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- The bacitracin susceptibility test is used to distinguish Group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci from other beta-hemolytic Streptococci.
- It can also be used to study the pattern of antibiotic susceptibility of various bacteria to Bacitracin.
- Since the vast majority of Micrococcus and Rothia organisms are susceptible to penicillin, and most coagulase-negative staphylococci are not, bacitracin differentiation may be effective for penicillin-susceptible strains.
Limitations of Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- Susceptibility testing should not be performed on old blood agar plates that have dried since the diffusion of antibiotics on such agar is reduced, resulting in false-negative results.
- With varied concentrations of Bacitracin, variable zone widths of inhibition may be detected; consequently, differential discs (0.04 U) should be used instead of sensitivity discs (10 U).
- Because light inoculum can cause a misleading zone of inhibition, sufficient inoculum with confluent growth should be employed.
- Serological testing, such as latex agglutination tests, should be used for further confirmation.
- On BAP, Staphylococci show no inhibition zone around the bacitracin 0.04-U disc. If Micrococcus is not incubated for the full 24 hours if MH agar is used, zones of inhibition larger than 7 mm but smaller than the 10-mm threshold can be achieved.
Bacitracin Susceptibility Test Citations
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/Manchester_Community_College_(MCC)/Remix_of_Openstax%3AMicrobiology_by_Parker%2C_Schneegurt%2C_et_al/11%3A_Control_of_Microbial_Growth/11.08%3A_Testing_the_Effectiveness_of_Antiseptics_and_Disinfectants
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26624026_Antibiotic_Resistance_of_Escherichia_Coli_Isolated_From_Poultry_and_Poultry_Environment_of_Bangladesh
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/p5ictnk/Bacitracin-differentiation-may-also-be-use-ful-for-penicillin-susceptible/
- https://quizlet.com/67731813/boc-microbiology-aerobic-gram-positive-cocci-flash-cards/
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7544871/
- https://foamid.com/2018/02/16/bactericidal-vs-bacteriostatic-antibiotics/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibiotic_sensitivity
- http://science.umd.edu/classroom/bsci424/LabManual/LabManualTextBody.doc
Related Posts
- Anisocytosis: Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
- Endospore Staining: Principle, Procedure, Reagents, Results
- Flow Cytometry: Overview, Principle, Steps, Types, Uses
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results
- MPV Blood Test: Calculation, High and Low MPV Value, Results
- Latex Agglutination Test: Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Iodine Test: Definition, Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar
- Biuret Test for Protein: Purpose, Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Reagents
- Streak Plate Method: Meaning, Principle, Methods, Importance, Limitations
- Bile Solubility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
- Butyrate Disk Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Beta Lactamase Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Limitations
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Bile Esculin Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses, Limitations