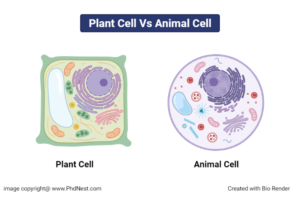
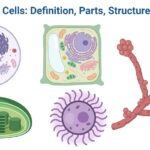
Plants and animals are built up of millions of cells, each with its own set of characteristics.
A significant aspect that defines their modes of multiplication is that they are both eukaryotic cells, which means they have a genuine nucleus that is enclosed and separated from other organelles by a nuclear membrane.
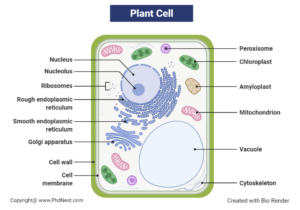
Plant Cell Diagram
They utilise their DNA, which is contained inside the cell nucleus, in identical mitosis and meiosis reproduction processes.
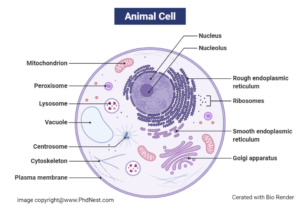
They’re both membrane-bound, having multiple cell organelles in common that execute comparable, though not identical, mechanisms to keep and govern the cells’ regular function. The nucleus, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, cytoskeleton, peroxisomes, and the cell membrane are among these organelles.
They also go through cellular respiration, which involves energy generating mechanisms that let the cell expand and operate normally.
How to increase Brain Power – Secrets of Brain Unlocked
Despite their many commonalities, they also have a few differences.
Plant and animal cells are physically similar since they are both eukaryotic cells. Both plant and animal cells contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and peroxisomes. Membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal components are all comparable in both. Membrane-bound organelles found in both plant and animal cells include the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and peroxisomes. The minor distinctions between plants and animals, on the other hand, are important and represent differences in cell functioning.
Animal Cell Diagram
Plant cells can grow to be bigger than animal cells. Animal cells have a usual range of 10 to 30 micrometres, while plant cells have a range of 10 to 100 micrometres. The fundamental structural distinctions between plant and animal cells are found in a few extra features found in plant cells, in addition to their size. Chloroplasts, the cell wall, and vacuoles are examples of these structures.
Differences between Plant cell and Animal cell : Structural and functional Differences
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
[ninja_tables id=”3898″]
Plant Cell vs Animal Cell Citations
• https://brainly.com/question/11566088
• https://answersdrive.com/what-is-the-difference-between-plant-and-animal-cells-7203906
• https://answersdrive.com/what-are-the-similarities-between-animal-and-plant-cells-7292357
• https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-a-plant-cell-373384
• https://www.thoughtco.com/vacuole-organelle-373617
• https://www.thoughtco.com/differences-between-mitosis-and-meiosis-373390
• https://www.thoughtco.com/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375
• https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-pits-and-plasmodesmata/
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
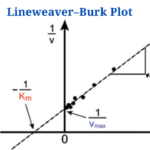
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
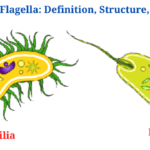
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
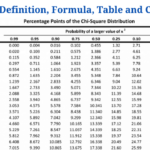
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
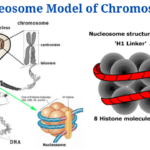
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results