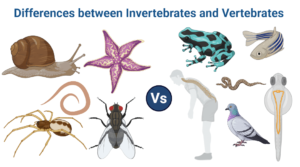
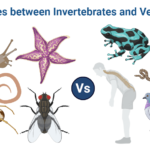
Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
Invertebrates (non-chordates) and vertebrates (living things) (Chordates) make up the majority of the animal kingdom. Those without a vertebral column or backbone are called invertebrates, while those with one are called vertebrates.
| Characteristics | Invertebrates (Non-Chordates) | Vertebrates (Chordates) |
| Radial | Bi-radial, or not present | Bilateral Symmetry |
| Metamerism | True or pseudo metamerism or not present | True metamerism |
| Post-anal tail | Not present | Generally there |
| Grade of organization | Protoplasmic or organ-system | Organ System |
| Germ Layers | Two (diploblastic), Three (Triploblastic) or not present | Three (Triploblastic) |
| Coelom | Acoelomate, pseudocoelomate or Truly coelomate | Truly coelomate |
| Limbs derivation | From the same segment | From numerous segments |
| Notochord | Notochord or Backbone not present | It is there at certain stage or substituted by a backbone prepared of ring-like vertebrae |
| Gut position | Dorsal to the nerve cord | Ventral to the nerve cord |
| Pharyngeal gill-slits | Not present | Is there at certain stage of life |
| Anus | Opens on the last segment or not present | Differentiated and opens prior to the last segment |
| Blood vascular system | Open, Closed or not present | Closed and to a great extent developed |
| Heart | Dorsal, Lateral or not present | Ventrally placed |
| Dorsal blood vessel | Blood flows anteriorly | Blood flows posteriorly |
| Hepatic portal system | Not present | Present |
| Hemoglobin | In plasma or not present | In red blood corpuscles |
| Respiration | Through body surface, gills or tracheae | Through gills or lungs |
| Nervous System | Solid | Hollow |
| Brain | Above pharynx or not present | Dorsal to pharynx in head |
| Nerve cord | Double, ventral, generally bearing ganglia | Single, dorsal, with no ganglia |
| Segmental nerve roots | Dorsal and ventral roots not separate | Dorsal and ventral roots separate |
| Reproduction | Asexual reproduction is main | Sexual reproduction is main |
| Regeneration power | Generally good | Generally poor |
| Body temperature | Cold-blooded | Cold or warm-blooded |
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
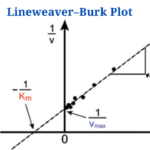
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
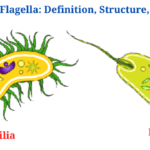
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results