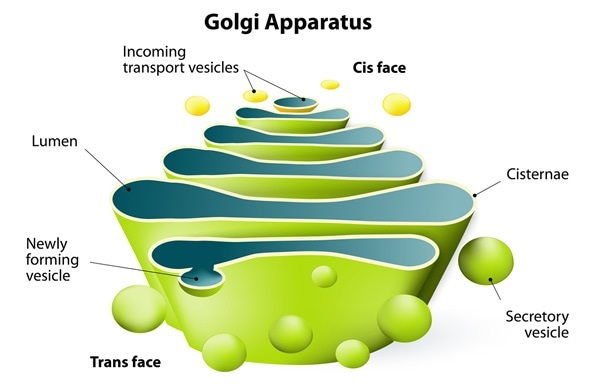
Golgi Apparatus: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
The Golgi apparatus has multiple names such as Golgi complex or Golgi body. The name is given on the name of the scientist, who discovered the organelle, i.e. Camillo Golgi. It is found in all the eukaryotic cells, plants as well as animals. They are membrane-bound organelle present in the cytosol of the cell. Let us … Read more