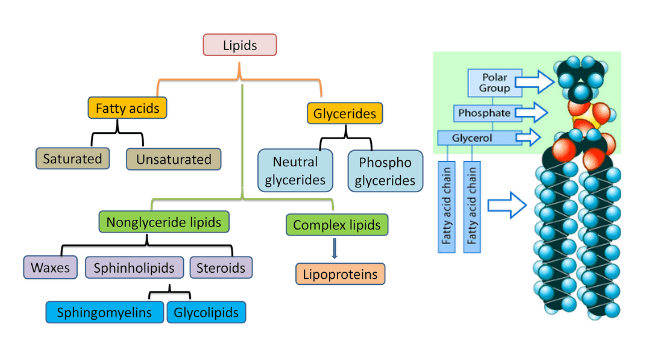
Lipids: Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Types, Functions, Examples
Table of Contents Definition of Lipids Lipids are a diverse collection of chemical molecules that are soluble in non-polar organic solvents but insoluble in water. They are employed as cell membrane components, energy storage molecules, insulation, and hormones in most plants, animals, and microbes. Lipids Characteristics At room temperature, lipids can be either liquids or … Read more