Digestive System Definition
The digestive system is uniquely designed to do its job, which is to turn the food into energy and nutrients that are essential for survival. Once the body absorbs the essential substances, it packages the solid waste for disposal through the bowel movement. Many organs work in complete harmony to let the digestive system function.
Digestion Definition
The conversion of complex food substances to simple absorbable forms is called digestion.
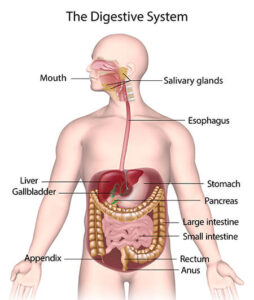
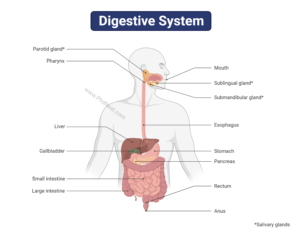
Digestive System Diagram
Digestive System Organs
Alimentary canal
- It begins with the mouth, which leads to a buccal cavity that has teeth & tongue.
- Thecodont – Tooth is embedded in the socket of the jaw bone.
- Diphyodont – Two sets of teeth (deciduous teeth & adult).
- Adult has 32 permanent teeth.
- Heterodont – Incisors, canine, premolar, molar.
- Dental formula – arrangement of teeth in each half of upper & lower jaw. 2123/2123.
- The hard chewing surface of teeth (enamel)- mastication of food.
- The tongue is freely movable attached to the oral cavity by the frenulum.
- Its upper surface has a small projection – papillae bear taste buds.
- The oral cavity led to the pharynx (common passage for food & air).
- Epiglottis is a cartilaginous flap that prevents the entry of food into glottis during swallowing.
- The esophagus is a thin, long tube passing through the neck, thorax, diaphragm and had to 1 shaped bag – stomach.
Stomach
- upper left portion.
- Gastro-oesophageal regulates the opening of the esophagus in the stomach.
- Cardiac portion- esophagus open.
- Fundic- main central region.
- Pyloric – Opens into small intestine’s first part.
Small intestine
- Duodenum – (-shaped, opening of the stomach in the duodenum by the pyloric sphincter.
- Jejunum – Long coiled middle portion.
- Ileum – Highly coiled. It opens in the large intestine.
Large intestine
- Caecum – Small blind sac that hosts some symbiotic microbes. Vermiform appendix (narrow finger-like tubular projection, vestigial organ) arises from the caecum. It opens in the colon.
- The colon – has four parts- an ascending, transverse descending, and sigmoid colon. Descending part opens in the rectum.
- Rectum – opens out through the anus.
Wall of alimentary canal
- Serosa- Outermost, mesothelium
- Muscularis – Smooth muscle(inward), longitudinal(outward).
- Submucosal – loose C.T. containing nerve, blood, lymph, glandless. But in some, like the duodenum, it has glands.
- Mucosa – innermost, forms rugae (irregular folds) in stomach and villi (finger-like folding). These cells produce numerous projections called microvilli, giving brush border appearance. They increase surface area. Villi are supplied with a network of capillaries and a large lymph vessel called a lacteal. Mucosal epithelium secretes mucus, which helps in lubrication. It also forms glands like gastric in the stomach and crypts in between villi in the intestine (crypts of Lieberkühn) & the stomach has an additional oblique layer.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Digestive Glands
Salivary glands
- Outside the buccal cavity, secrete juice into the cavity.
- Parotids – Cheeks
- Sub maxillary(modular) – Lower jaw
- Sublingual – Below tongue.
Liver
- Largest gland, about 1.2 – 1.5 Kg, below diaphragm in the abdominal cavity and has two lobes. Hepatic lobules are structures and functional units containing hepatic cells in the form of cords.
- Each lobule is covered by a thin C.T. called Glisson’s capsule.
- Bile pathway – Hepatic cells- hepatic ducts – stored in the gall bladder (muscular sac)- common bile duct.
- The bile duct & pancreatic duct open into the duodenum as common hepatic, pancreatic duct guarded by the sphincter of Oddi.
Pancreas
- Between limbs of the duodenum, compound (exocrine + endocrine)
- Exocrine – Secrete alkaline pancreatic juice (enzyme).
- Endocrine – Secrete hormones, insulin, Glucagon.
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
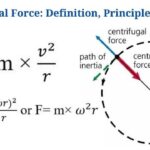
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results