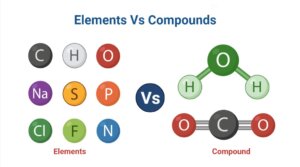
Definition of Elements (What is Element?)
Elements are pure substances made up of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down chemically into smaller components.
- Elements are chemical species that mix with others to generate more complex species such as compounds as well as molecules.
- The atomic number, or the number of protons in the nucleus, is used to classify elements.
- The quantity of protons determines the element’s electric charge, as it determines the number of non-ionized electrons.
- The sort of elements contained in chemical substances determines their physical as well as chemical features.
- So far, 118 elements have been identified, 94 of that are naturally occurring as well as can be found in various forms.
- The naturally occurring elements are created by a variety of natural nucleosynthesis mechanisms.
- Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids on a periodic table based on their properties.
- At standard temperatures as well as pressures, the majority of elements exist in a solid state. Several elements, such as bromine as well as mercury, exist in a liquid state, whereas others exist in a gaseous state.
- Names are assigned to elements, as well as symbols and numbers are used to represent them.
- Elements are necessary for the production of compounds as well as larger substances, that then make up all of the stuff on the planet.
- Minerals as well as micronutrients such as iron, potassium, as well as zinc are found in living systems.
- Oxygen, nitrogen, iron, gold, as well as other elements are examples of elements.
Definition of Compounds (What is Compound?)
Compounds are chemical compounds made up of two or more atoms of the same or different elements that are chemically bonded together.
- The sort of elements included in compounds, as well as the type of chemical bonding, define them. Depending on the type of link, compounds can be ionic, covalent, or metallic. Compounds‘ physical as well as chemical properties are also determined by their bonding.
- Compounds can be created by combining atoms of the same or different elements or by a chemical interaction between two or more compounds.
- The breaking of old bonds as well as the formation of new ones results in the formation of new compounds as a result of a reaction between two existing compounds.
- More than 3000 compounds have been registered for use around the world, as well as they are made up of various combinations of known components.
- Most compounds have a fixed stoichiometric proportion that remains constant regardless of the compound’s source.
- Chemical formulae are used to represent compounds as well as provide information on the type as well as quantity of atoms present.
- Compounds can be broken down into elements in a variety of ways, both chemically as well as physically.
- Compounds are impure substances since they are made up of many elements.
- Chemical formulae, that incorporate the element symbols as well as their proportions, are used to depict various compounds.
- Chemical compounds are also distinguished by chemical structures that are kept together by chemical bonds. These have diverse topologies depending on the sort of bond that holds distinct elements in a compound together.
- Water, carbon dioxide, ammonia, magnesium sulfate, as well as other chemicals are common examples.
Key Differences between Elements and Compounds
(Elements Vs Compounds)
[ninja_tables id=”5657″]
Elements Examples
Oxygen
- Oxygen is a chemical element with the atomic number 8 as well as the symbol O that is a highly reactive nonmetal.
- It is the universe’s third most plentiful element. It is an oxidizing agent that can produce oxides with a variety of elements as well as compounds.
- Oxygen is a colorless as well as odorless gas that is required for a variety of biochemical functions in the human body.
- In addition, it is the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere. Carl Wilhelm Scheele, a Swedish chemist, discovered it in 1772 while researching potassium nitrate as well as mercuric oxides.
- The oxygen atom’s nucleus is made up of eight protons as well as neutrons. Eight electrons orbit the nucleus, revolving in separate orbits.
- Photosynthesis, that produces oxygen in the presence of sunshine, carbon dioxide, as well as water, replenishes oxygen on Earth.
- Oxygen, in the form of water, is a significant element in living processes. The most significant oxygen compound is water.
Compounds Examples
Ammonia
- Ammonia is made up of a 1:3 ratio of nitrogen as well as hydrogen. The compound’s molecular formula is NH3.
- Ammonia is a prevalent nitrogenous waste product in nature, especially among aquatic creatures.
- As a precursor to food as well as fertilizers, it is utilized to give nutritional needs to terrestrial organisms.
- Ammonia is a colorless gas with a distinctive strong odor at normal temperature.
- The presence of strong hydrogen bonding between the molecules, however, allows it to be easily liquefied.
- The ammonia molecule has a 106.7° bond angle as well as is trigonal pyramidal in form. Since it forms a hydrogen bond with other ammonia molecules, the molecule is polar.
Elements Vs Compounds Citations
- Gautum SD, Pant M and Adhikari NR (2016). Comprehensive Chemistry, Part 2. Sixth Edition. Heritage Publishers and Distributors Pvt. Ltd
- https://www.nuclear-power.net/Oxygen-properties/
- https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-element-and-vs-molecule/
- https://www.thoughtco.com/protons-neutrons-and-electrons-in-an-atom-603818
- https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/what-are-some-examples-of-compounds-131353
- https://www.chemicool.com/definition/compound.html
- https://www.austincc.edu/lesalbin/CHEMISTRY%20REVIEW.htm
- https://www.ausetute.com.au/elements.html
- https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-elements-and-compounds-with-example/
- https://quizlet.com/27719928/elements-compounds-mixtures-flash-cards/
- https://infogalactic.com/info/Chemical_element
Related Posts
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Ethanol Vs Methanol: Definition and 10+ Differences
- Hydrogen Bond: Properties, Definition, Types, Examples
- Nitrate Vs Nitrite: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Aromatic Compounds vs Aliphatic Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Compound Vs Mixture: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Elements Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Molecules Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Hard water Vs Soft water: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Glucose Vs Sucrose: Definition and Key Differences
- 13+ Difference Between Atom and Molecule with Examples
- How to Balance Chemical Equation: Methods, Steps, Examples
- Ionic Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
- Amylase Vs Amylose: Definition, Differences, Example