Iodine Test Definition
The iodine test is a chemical method for separating mono- as well as disaccharides from polysaccharides such as amylase, dextrin as well as glycogen. The starch-iodine test is a version of this test which is used to test the existence of glucose produced by plants in the leaves.
Iodine Test Objectives
- Existence of polysaccharides, especially starch, must be detected.
Iodine Test principle
- Polyiodide ions form colourful adsorption complexes with helical chains of glucose residue of amylase (blue-black), dextrin (black), or glycogen in the iodine test (reddish-brown).
- Colorless monosaccharides, disaccharides, as well as branching polysaccharides like cellulose. The colour of Amylopectin is orange-yellow.
- Lugol’s iodine, an aqueous solution of elemental iodine as well as potassium iodide, is the reagent which we use in iodine test.
- Iodine is not soluble in water on its own. When potassium iodine is added, the iodine ion reversibly combines with iodine to generate a triiodide ion that afterwards react with another iodine molecule to form a pentaiodide ion.
- Iodide, triiodide, as well as pentaiodide ions are colourless, whereas the bench iodine solution looks brown.
- Helix (coil or spring) structure of the glucose chain seems to be crucial to Iodine test.
- Furthermore, the colour generated is decided by the length of the glucose chains.
- Ions generated, triiodide as well as pentaiodide, are linear as well as slip within the helix structure.
- Exchange of charge among the helix as well as the polyiodide ions is thought to cause changes in the spacing of the energy levels, which allow the complex to absorb visible light as well as give it its colour.
- With increasing temperature as well asthe addition of water-miscible organic molecules like ethanol, the colour severity falls.
- The blue colour amylase-iodine complex dissociates once heated, yet assembles again once cooled since the helical shape is broken; consequently, amylose loses its capability to bind iodine and blue colour.
- Cooling restores the blue hue due to the recovering of the helical structure as well asthe recovery of iodine binding capacity.
Requirements
1 . Reagent
- Lugol’s iodine is made by mixing 5% elemental iodine with 10% potassium iodide to make Lugol’s iodine.
- Test sample
2. Supplies Needed
- Test Tubes for testing
- Test tube stand
3. Equipment
- Water bath
Iodine Test Procedure
- Fill a clean, dry test tube with 1 mL of a specified sample.
- Control 1 mL of pure water in a separate tube.
- Fill both tubes with a few drops of Lugol’s solution and vortex them together.
- Look at the colour in the test tubes to see how it looks.
- Heat the test tubes in a water bath until the colour fades.
- Set the test tubes aside to cool.
- Take note of how the test tubes appear to be coloured.
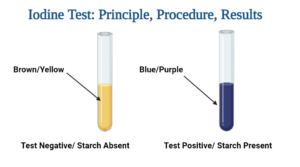
Iodine Test Results and Analysis
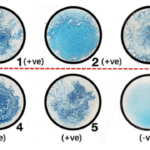
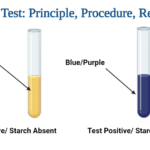
- A positive test shows the existence of starch when a blue-black or purple tint appears.
- When no colour change occurs, it is negative result and shows a lack of starch.
Iodine Test Applications
- This test measures the level of starch in a variety of samples.
- Likewise, the test is used to evaluate the photosynthesis process in plants.
Iodine Test Limitations
- This test can’t be done in acidic settings since the starch hydrolyzes in that environment.
- This is a qualitative test that does not indicate starch content.
Iodine Test Citations
- https://alevelbiologynotes.com/testing-for-biological-molecules/
- https://allmedicalstuff.com/barfoeds-test/
- https://www.scribd.com/document/429888468/Advances-in-Carbohydrate-pdf
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/p39m2q7c/IKI-Test-experiments-the-presence-of-starch-in-a-solution-if-positive-color/
- https://libraryofessays.com/lab-report/lap-report-1895512
Related Posts
- Anisocytosis: Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
- Endospore Staining: Principle, Procedure, Reagents, Results
- Flow Cytometry: Overview, Principle, Steps, Types, Uses
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results
- MPV Blood Test: Calculation, High and Low MPV Value, Results
- Latex Agglutination Test: Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Iodine Test: Definition, Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results
- Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar
- Biuret Test for Protein: Purpose, Objectives, Principle, Procedure, Reagents
- Streak Plate Method: Meaning, Principle, Methods, Importance, Limitations
- Bile Solubility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
- Butyrate Disk Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Beta Lactamase Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Limitations
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses, Limitations
- Bile Esculin Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses, Limitations