Microvilli Definition
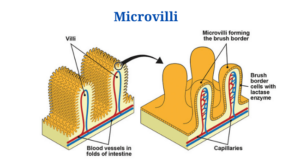
- Microvilli are minute projections that exist in, on, and around cells, to put it simply.
- They can be found alone or in combination with villi (projections of some mucous membranes, most specifically of the small intestine, which are tiny folds that project out like numerous fingers).
- Microvilli are even tiny folds that shoot out like fingers on each of the villi.
- Microvilli can be seen in the small intestine, egg cell surfaces, and white blood cells.
- The brush border is a feature seen on the apical surface of some epithelial cells, such as those in the small intestines, made up of thousands of microvilli.
Structure of Microvilli
- Microvilli are a diversified set of protuberances on the surface of various tissues that are tightly packed.
- They are usually shorter and have a smaller diameter than cilia. They have a diameter of around 0.1 m and a length of a fraction of a micrometre to about 2 m.
- Microvilli are actin fibre bundles that are cross-linked.
- Despite their status as cellular extensions, microvilli contain few or no cellular organelles.
- They do, however, have their own plasma membrane that contains cytoplasm and microfilaments.
- The structural core of each microvillus is a dense bundle of cross-linked actin filaments.
- The core of the microvilli consists of 20 to 30 densely packed actin filaments that are cross-linked by the bundling proteins fimbrin (or plastin-1), villin, and espin.
- The cytoplasm contains actin filaments, which are most plentiful at the cell surface. The form and movement of the plasma membrane are thought to be controlled by these filaments.
- Actin fibres are formed in reaction to external stimuli, allowing a cell to change its shape to fit a certain scenario.
- The structural core of the enterocyte microvillus is connected to the plasma membrane along its length by lateral arms made of myosin 1a and calmodulin, a Ca2+ binding protein.
- The intermicrovillous space is the gap between microvilli on a cell’s surface. When myosin II and tropomyosin contract, intermicrovillous space increases, and when contraction stops, it diminishes.
Microvilli Functions
- The minute microvilli enhance the surface area of the cell, which helps with absorption and secretion.
- They collaborate with villi in the intestine to absorb more nutrients and substances by increasing the surface area of the intestine.
- The enzymes in the microvillar membrane help to break down complex nutrients into simpler, easier-to-absorb forms.
- Glycosidases, for example, are carbohydrate-digesting enzymes that can be found in high concentrations on the surface of microvilli in enterocytes.
- Microvilli increase the number of digestive enzymes that can be present on the cell surface as well as the amount of cellular surface area available for absorption.
- They have a role in egg cells because they aid in the anchoring of sperm to the egg, making fertilisation easier.
- The microvilli in white blood cells serve as anchoring points. White blood cell movement is aided by them.
- The storage of membrane and microfilament materials is the second sort of hypothesised function. Microvilli also have the ability to move. Unwanted materials may be swept toward a resorptive portion of the cell by the microvilli on the cell surface. They also perform a range of additional tasks, such as absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion, and mechanotransduction.
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Microvilli Citations
- http://biology.kenyon.edu/edwards/project/greg/pd.htm
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/microvilli-definition-function.html
- http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/micvil.html
- https://www.easybiologyclass.com/difference-between-cilia-and-microvilli-comparison-table/
- http://www.biologydiscussion.com/cell/cell-surface/3-types-of-cell-surface-projection-cell-biology/26375
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
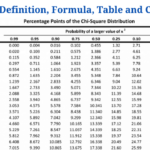
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
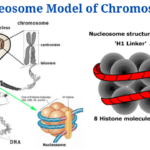
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
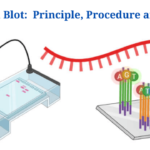
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results