Definition of Physical Change
A physical alteration is a procedure which alters a substance’s physical form but not its chemical content.
- The molecules of a substance are rearranged during a physical change, but the chemical content of the substance stays constant.
- A physical change typically entails a change in physical attributes such as strength, condition, shape, size, colour, as well as so on.
- Physical changes can be reversed, but reversibility cannot be employed as a categorization criterion since some changes are irreversible.
- The rearrangement of atoms is involved in physical changes involving changes in the form, size, as well as state of molecules.
- No new substances are generated since the chemical composition of a substance does not change as a result of physical change.
- Since physical changes are usually transient, the amount of energy received or released during them is substantially lower.
- Melting ice, breaking glass, boiling water, as well as other physical changes are instances of physical changes.
Definition of Chemical Change
A chemical change takes place when the chemical composition of a substance changes, resulting in the formation of a new compound.
- Chemical change can take the form of chemical synthesis or breakdown. Chemical synthesis is the process of combining two or more chemical ingredients to create a new compound. The breakdown of a chemical compound into two or more distinct components is known as chemical decomposition.
- Chemical changes, also known as chemical reactions, are mostly irreversible but can be reversed in some cases.
- The atoms of a substance are rearranged during a chemical change, as well as the change is accompanied by a change in energy. Depending on whether they absorb or release energy, chemical reactions can be classified as endothermic or exothermic.
- Inorganic changes, organic changes, as well as biochemical changes are the three types of chemical changes.
- Inorganic changes are reactions between elements as well as compounds which typically take place in laboratories or large-scale manufacturing facilities.
- Organic chemical changes are processes involving carbon, hydrogen, as well as a few additional elements in organic molecules.
- Biochemical alterations are the responses which occur in living organisms as they grow as well as modify their metabolism. Enzymes as well as hormones are usually in charge of regulating biochemical reactions.
- Chemical changes include things like burning paper, digestion, electroplating, as well as so on.
Key Difference between Physical Change and Chemical Change
Physical Change Vs Chemical Change
[ninja_tables id=”5588″]
Physical Change Examples
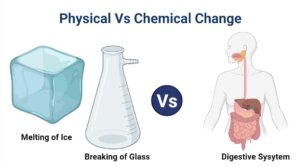
Melting of Ice
- When ice melts, the shape as well as state of water change, but the chemical makeup remains the same.
- The melting as well as freezing processes make it simple to convert ice to water as well as water to ice.
- It is a physical alteration since it is reversible as well as does not alter the substance’s chemical composition.
- Since the water molecules in ice are closer together than those in water, changes in their position but not their number occur.
- The absorption of energy in the form of heat energy takes place during the conversion of ice to water
Chemical Change Examples
Digestion
- Digestion is the process of conversion of large macromolecules into smaller molecules in the presence of specific enzymes.
- It is a chemical change as the chemical composition of the substances changes as the larger molecule is broken down into smaller particles.
- The change is a biochemical change whichtakes place in almost all living organisms throughout the world. In higher organisms, the process takes place within a system where a number of organs work together to complete the process.
- In lower organisms, the process is less complex as these utilize comparatively less complex substances.
Physical Change and Chemical Change Citations
- https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-physical-change-605910
- https://tutors.com/lesson/chemical-change-definition-properties-examples
- https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/5d7024989f07ce001bd403a8/bio-unit-1-quiz
- https://www.mysolutionguru.com/ps/physical-and-chemical-changes/252
- https://www.mariaregina.org/ourpages/auto/2016/6/9/48988952/Final_Review_tc_2_.pdf
Related Posts
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Ethanol Vs Methanol: Definition and 10+ Differences
- Hydrogen Bond: Properties, Definition, Types, Examples
- Nitrate Vs Nitrite: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Aromatic Compounds vs Aliphatic Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Compound Vs Mixture: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Elements Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Molecules Vs Compounds: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Hard water Vs Soft water: Definition, Differences, Examples
- Glucose Vs Sucrose: Definition and Key Differences
- 13+ Difference Between Atom and Molecule with Examples
- How to Balance Chemical Equation: Methods, Steps, Examples
- Ionic Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
- Amylase Vs Amylose: Definition, Differences, Example