What is RFLP ? Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
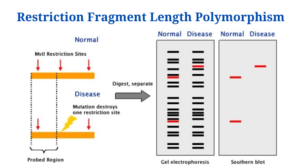
- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique for distinguishing species by analysing patterns produced from DNA cleavage.
- It’s a strategy that takes use of differences in homologous DNA sequences.
- The presence of alternative alleles associated with restriction fragments of different sizes defines a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Simply put, RFLP refers to differences in the length of restriction DNA fragments between members of a species.
- In a restriction digest, a restriction enzyme fragments a sample of DNA by recognising and cutting DNA wherever a specified short sequence occurs.
- The resultant DNA fragments are then separated by length using an agarose gel electrophoresis procedure before being transferred to a membrane using the Southern blot approach. The length of the corresponding probe fragments is determined when the membrane is hybridised to a tagged DNA probe.
- When the length of a detected fragment differs between persons, an RFLP results.
- RFLP analysis was the first DNA profiling approach that was affordable enough to seek widespread application, despite the fact that it is now essentially obsolete due to the emergence of inexpensive DNA sequencing technology.
Principe of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
When DNA is digested by a restriction enzyme, the length of the fragments produced will differ if the distance between sites of cleavage of a given restriction endonuclease differs between two organisms. The patterns generated can be utilised to distinguish between species (and even strains) based on their resemblance and differences.
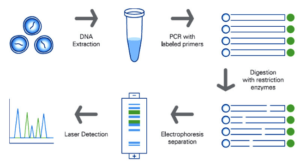
A Step-by-Step Guide to Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
- The initial stage in this procedure is to separate the target’s DNA.
- After the DNA has been extracted from the sample, restriction digestion with restriction enzymes is performed.
- The digested DNA sample is next subjected to gel electrophoresis, which divides the DNA into different sizes. A large number of DNA fragments with small length differences are produced.
- After that, the gel is subjected to a reagent that denatures double-stranded DNA into single-stranded DNA.
- Southern blotting, which involves transferring DNA from the gel to a nylon membrane, is the next step.
- After that, the nylon membrane is immersed in solution with radioactive complementary nucleotide probes that hybridise to specific DNA sequences on the membrane.
- The membrane is then put against X-ray film, which is exposed by hybridised radioactive probes, resulting in an autoradiogram.
- RFLP analysis is used to find pattern differences and confirm polymorphisms.
Applications of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP analysis was once widely used in genome mapping, gene localisation for genetic diseases, illness risk assessment, and paternity testing.
RFLP can be utilised in a variety of circumstances to achieve a variety of goals:
- To determine the source of a DNA sample in paternity trials or criminal prosecutions. (In other words, it can be used in forensics).
- Identifying an individual’s illness status. (For example, it can be used to detect mutations)
- The distance between RFLP loci is used to calculate recombination rates, which can be used to create a genetic map.
- In the study of animal populations’ genetic diversity and breeding habits.
- RFLP was created to map the chromosomes of humans, mice, maize, tomato, rice, and other organisms.
Benefits of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ( RELP)
- The fundamental benefit of RFLP analysis over PCR-based techniques is that it doesn’t require any prior sequence knowledge or oligonucleotide synthesis.
- Rather than phenotypes, the results are based on trustworthy genotypic traits.
- Genetic Marker based on RFLP
- Because RFLP is a co-dominant marker, it can be used to estimate heterozygozity.
- In Genomic DNA Sequence, RFLP is a highly useful study.
- Highly reliable methodology that is easily transferable between labs.
Restrictions (Limitations) Polymorphism in Fragment Length ( RFLP )
- Slow
- Cumbersome
- Requires a big amount of DNA from the sample.
- It is not possible to automate.
- Some animals have low levels of polymorphism.
- Only a few loci were found per test.
- A sufficient probe library is required.
- The following procedures are required: probe labelling, DNA fragmentation, electrophoresis, blotting, hybridization, washing, and autoradiography.
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Citations
- https://www.slideshare.net/orampo/restriction-fragment-length-polymorphism-29253376
- http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/staff/dave/roanoke/genetics980211.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restriction_fragment_length_polymorphism
- https://www.princeton.edu/~lsilver/book/MG8.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/ArunimaSur/rflp-rapd
- https://cropgenebank.sgrp.cgiar.org/images/file/learning_space/molecular_markers/volume1/RFLPs.pdf
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results