Vacuoles Definition:
- A vacuole is a film-bound organelle that is available in all plant and contagious cells and some protist, creature, and bacterial cells.
- The most prominent compartment in most plant cells is an extremely huge, liquid-filled vacuole.
- Huge vacuoles are likewise found in three genera of filamentous sulfur microorganisms, the Thioploca, Beggiatoa, and Thiomargarita.
- Nonetheless, the capacity and meaning of vacuoles change enormously as indicated by the sort of cell having a lot more noteworthy noticeable quality in the cells of plants, organisms, and certain protists than those of creatures and microorganisms.
- There might be a few vacuoles in a solitary cell. Every vacuole is isolated from the cytoplasm by a solitary unit film, called the tonoplast.
- By and large, they possess more than 30% of the cell volume; yet this might change from 5% to 90 percent, contingent upon the cell type.
Structure of Vacuoles
- They for the most part have no essential shape or size; their construction shifts as indicated by the prerequisites of the cell.
- In youthful and effectively separating plant cells the vacuoles are minuscule.
- These vacuoles emerge at first in youthful separating cells, presumably by the reformist combination of vesicles got from the Golgi contraption.
- A vacuole is encircled by a layer called the tonoplast or vacuolar film and loaded up with cell sap.
- The tonoplast is the cytoplasmic layer encompassing a vacuole, isolating the vacuolar substance from the cell’s cytoplasm.
- As a layer, it is primarily associated with controlling the development of particles around the cell and segregating materials that may be destructive or a danger to the cell.
- Vacuoles are basically and practically identified with lysosomes in creature cells and may contain a wide scope of hydrolytic chemicals.
- Furthermore, they ordinarily contain sugars, salts, acids, and nitrogenous mixtures like alkaloids and anthocyanin colors in their cell sap.
- The pH of plant vacuoles might be just about as high as 9 to 10 because of huge amounts of antacid substances or as low as 3 because of the amassing of amounts of acids (e.g., citrus, oxalic, and tartaric acids).
Click Here for Complete Biology Notes
Types of Vacuole:
Sap Vacuole:
- It has various vehicle frameworks for the entry of various substances.
- Various little sap vacuoles happen in creature cells and youthful plant cells.
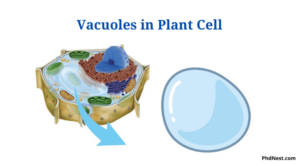
- In mature plant cells, the little vacuoles wire to shape a solitary enormous focal vacuole which involves up to 90% of the volume of the cell.
- The huge focal vacuole extends the cytoplasm as a far fringe layer. This is a gadget to work with quick trade between the cytoplasm and the general climate.
- The liquid present in the sap vacuoles is frequently called sap or vacuolar sap.
Diagram: Vacuoles in Plan Cell
Contractile Vacuoles:
- They happen in some protistan and algal cells discovered for the most part in freshwater.
- A contractile vacuole has a profoundly extensible and folding film.
- It is additionally associated with a couple of taking care of channels (e.g., Paramecium).
- The taking care of trenches acquires water with or without byproducts from the encompassing cytoplasm.
- They empty something very similar into the contractile vacuole. The vacuole balloons. The cycle is called diastole.
- The enlarged contractile vacuole interacts with the plasma layer and implodes. Imploding is called systole. This tosses the vacuolar substance to the outside.
- Contractile vacuoles partake in osmoregulation and discharge.
Top Online PhD Programs : Pros and Cons, Universities, Courses, Career.
Air Vacuoles:
- They happen in the cells of protozoan protists, a few lower creatures, and phagocytes of higher creatures.
- A food vacuole is framed by the combination of a phagosome and a lysosome.
- The food vacuole contains stomach-related chemicals with the assistance of which supplements are processed.
- The processed materials drop into the encompassing cytoplasm.
Vacuoles Functions:
- A plant vacuole has an assortment of capacities.
- Various vacuoles with particular capacities are likewise regularly present in a similar cell.
- Plant vacuoles can store many sorts of particles. It can go about as a capacity organelle for the two supplements and side effects.
- A portion of the items put away by vacuoles has a metabolic capacity.
- For instance, delicious plants open their stomata and take up carbon dioxide around evening time (when happening misfortunes are not exactly in the day) and convert it to malic corrosive.
- This corrosive is put away in vacuoles until the next day when light energy can be utilized to change it over to sugar while the stomata are kept closed.
- Specifically, they can sequester substances that are possibly unsafe to the plant cell, in case they are available in mass in the cytoplasm.
- The vacuole has a significant homeostatic capacity in plant cells that are exposed to wide varieties in their current circumstance.
- For instance, when the pH in the climate drops, the transition of H+ into the cytoplasm is supported by an expanded vehicle of H+ into the vacuole.
- Many plant cells keep up with turgor pressure at momentous steady levels notwithstanding huge changes in the constitution of the liquids in their nearby climate by changing the substantial pressing factor of the cytoplasm and vacuole—to some extent by controlled breakdown and resynthesis of polymers like polyphosphate in the vacuole, and partially by adjusting.
- By expanding in size, vacuoles permit the sprouting plant or its organs (like leaves) to become rapidly and spending generally water.
- In seeds, put away proteins required for germination are kept in ‘protein bodies’, which are adjusted vacuoles.
In Other Cells:
In Fungal Cell: They are associated with many cycles including the homeostasis of cell pH and the centralization of particles, osmoregulation, putting away amino acids and polyphosphate, and degradative cycles.
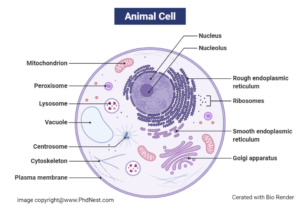
In Animal Cell: Vacuoles perform for the most part subordinate jobs, aiding bigger cycles of exocytosis and endocytosis.
Vacuole Citations
- Alberts, B. (2004). Essential cell biology. New York, NY: Garland Science Pub.
- Kar,D.K. and halder,S. (2015). Cell biology genetics and molecular biology.kolkata, New central book agency
- Alberts, Bruce, Johnson, Alexander, Lewis, Julian, Raff, Martin, Roberts, Keith, and Walter, Peter (2008). Molecular Biology of the Cell (Fifth Edition), (Garland Science, New York), p. 781
- http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_vacuole.html
- http://www.biologydiscussion.com/cell/vacuoles-in-cytoplasm-4-types-organelles/70424
- https://quatr.us/biology/vacuole-cell-biology.htm
Related Posts
- Phylum Porifera: Classification, Characteristics, Examples
- Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope) Definition, Principle, Uses, Parts
- Epithelial Tissue Vs Connective Tissue: Definition, 16+ Differences, Examples
- 29+ Differences Between Arteries and Veins
- 31+ Differences Between DNA and RNA (DNA vs RNA)
- Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Parts, Structure, Examples
- Centrifugal Force: Definition, Principle, Formula, Examples
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction: Overview, 18+ Differences, Examples
- Glandular Epithelium: Location, Structure, Functions, Examples
- 25+ Differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
- Lineweaver–Burk Plot
- Cilia and Flagella: Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram
- P-value: Definition, Formula, Table and Calculation
- Nucleosome Model of Chromosome
- Northern Blot: Overview, Principle, Procedure and Results